In This Blog
- What is anxiety of alcohol, and what is its importance
- How alcohol causes a reaction to anxiety
- Short and long term alcohol induced anxiety effects
- Relationships of anxiety, mental and substance use
- In which type of scenario(s) support and recovery-focused care may be beneficial
Alcohol doesn’t just affect one’s ability to coordinate their movements or get a good night’s sleep; it also has a strong effect on their anxiety and emotional regulation. For many people, alcohol often acts to decrease one’s stress level initially, but a feeling of nervousness, restlessness, or panic soon brings that on.
Understanding the relationship between alcohol and anxiety is important so people are aware of the symptoms and can make an informed decision regarding treatment, recovery and long-term emotional development.
What is Anxiety, and Why Does It Matter?
Anxiety is a common stress response, which is a useful way of keeping the body alert. When anxiety can be frequent and/or intense, it can interfere with the course of everyday life, emotional balance and physical health.
Alcohol and anxiety go hand in hand because alcohol has an impact on the chemistry within the brain and the stress response. In the long term, alcohol use can make things worse, not better.
Anxiety can be temporary, but when reinforced by alcohol, it can be a persistent type of feeling.
How Does Alcohol Trigger Anxiety in the Body?
Alcohol directly acts on the mood- and stress-regulating neurotransmitters. While alcohol intake can be used to calm someone who is really wound up, alcoholism is commonly used to cause anxiety due to its withdrawal from the body.
Key Mechanisms
- Alcohol causes an imbalance between GABA and glutamate.
- Stress hormones increase when going through withdrawal
- Changes in blood sugar that give rise to the feeling of anxiety
- Less sleep causes high nervous system activity.
These changes produce a state in which the brain is always on alert when drinking has taken place.
Fact: Alcohol can worsen anxiety symptoms in up to one-third of regular drinkers.
Source: National Institutes of Health (NIH)
How Alcohol Affects the Stress – Anxiety Connection
Alcohol is anti to the stress-regulating mechanism of the body. The nervous system becomes less effective at calming itself naturally.
Why This Matters
- Anxiety appears to be increased post-drinking
- Stress tolerance decreases
- Loss of emotional control
- Panic-like symptoms may appear
Research from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) shows that alcohol-related anxiety is linked to nervous-system dysregulation.
100% Confidential Support is Available 24/7
No matter what you’re going through, you’re not alone. Our dedicated team is here to provide a safe, judgment-free space where you can talk openly and honestly. Whether you need emotional support, resources, or just someone to listen.
We’re here for you—completely confidential and always respectful of your privacy. Call us today!
Alcohol’s Impact on Anxiety-Related Systems
Body System | Alcohol’s Effect | Anxiety Outcome |
Brain | Neurotransmitter imbalance | Increased nervousness |
Nervous system | Stress hormone rebound | Restlessness, panic |
Sleep system | Fragmented sleep | Heightened anxiety |
Blood sugar | Sudden drops | Shakiness, fear |
Emotional regulation | Reduced coping ability | Mood instability |
How Alcohol-Related Anxiety Affects Mental
Alcohol related anxiety doesn’t stay only for short-term discomfort. In the long run, this can make oneself prone to having generalized anxiety, which makes oneself exposed to panic symptoms as well as low mood.
The imbalance of neurochemicals from the alcohol may lead to an anxiety reaction that leads to the feeling of being stressed. It could be the reason why consuming alcohol as a way of dealing with anxiety could turn into a major reason for getting anxiety.
What Are the Short-Term Signs of Alcohol-Related Anxiety?
These short-term symptoms of anxiety may be within a few hours or the next day following the consumption.
Common Indicators
- Racing thoughts
- Increased heart rate
- Irritability or unease
- Difficulty focusing
- Trouble sleeping
The symptoms mostly tend to go off as the alcohol leaves the system; however, there is a great risk if the things are repeated.
Long-Term Effects of Alcohol-Driven Anxiety
With further alcohol use, anxiety symptoms could get more frequent and more severe.
Potential Long-Term Impacts
- Constant Nervousness/Worrying
- Panic symptoms
- Sleep disturbances
- Reduced stress tolerance
- Increased reliance on alcohol for relief
FACT: Studies indexed in PubMed show that long-term alcohol use is linked to higher anxiety severity and relapse risk.
Short- vs Long-Term Anxiety Effects of Alcohol
Time Frame | Anxiety Impact |
Short-term | Temporary nervousness |
Repeated use | Heightened stress response |
Long-term | Chronic anxiety patterns |
Recovery phase | Gradual anxiety reduction |
Explore whole-person recovery support with Solutions Healthcare
Does Alcohol-Related Anxiety Improve After Stopping Drinking?
In many cases, the moment one is not using alcohol, the symptoms of anxiety do not exist anymore. The brain is able to overcome it with some rest, nutrition, and emotional care.
Recovery Factors
- Length of Alcohol abuse/ Duration and intensity of alcohol abuse
- Baseline anxiety levels
- Sleep quality
- Stress exposure
- Access to behavioral care support
Some people have relief in weeks, although standing anxiety takes a while to be stabilised.
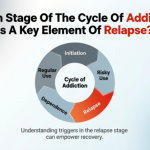
The Link Between Anxiety, Stress, and Alcohol Use
Stress and alcohol also tend to feed on one another. Alcohol may have a calming effect, but when it wears off, the symptoms of anxiety come back.
This creates a cycle:
- Stress increases anxiety
- Alcohol provides a temporary relief to them
- Anxiety returns stronger
- Drinking repeats
Over time, this cycle worsens (both emotionally and physically).
Expert’s Advice: “Alcohol use can intensify anxiety symptoms and delay emotional recovery.” NIAAA

When Anxiety Signals a Need for Support
Occasional anxiety is quite common, but if the symptoms recur, then it may be a symptom of some deeper cause.
Signs to Take Seriously
- Anxiety, which is experienced most often after the use of alcohol
- Panic symptoms increase
- The inability to reduce the quantity of alcohol
- Anxiety gets in the way of everyday life
- Sleep and mood worsen
Behavioral support can target both anxiety and alcohol patterns
How Recovery-Focused Care Supports Anxiety Treatment
Recovery programs address anxiety by giving a backbone to the nervous system as well as finding more ways for it to cope with them.
Supportive Elements
- Reduced alcohol exposure
- Anxiety-management skills
- Stress-reduction techniques
- Sleep stabilisation
- Long-term behavioural planning
This way is good for restoring the emotional balance instead of covering up.
Get anxiety-aware addiction support through Solutions Healthcare
When the effects of an alcohol-related anxiety have begun to take their toll on one’s emotional or daily functioning, then structured support is needed to restore balance. Solutions Healthcare is an evidence-based behavioral and alcohol-specific recovery service provider, and also supports the treatment of anxiety, stress, and recovery planning.
Medical Disclaimer: This blog is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Key Takeaways
- Alcohol can make your anxiety get worse, even though it will help settle you down in the short term.
- Anxiety symptoms often appear after drinking
- Repeated alcohol consumption leads to a long-term risk of anxiety
- Stopping alcohol allows anxiety to improve gradually
- Get some professional support if symptoms continue to last longer than 4 – 6 weeks
FAQs
1. How does alcohol cause inflammation in the body?
Alcohol disrupts immune regulation, increases gut permeability, and triggers the release of inflammatory cytokines. These processes activate the body’s defense systems beyond what’s needed, leading to ongoing inflammation that can affect multiple organs and emotional regulation when alcohol use is repeated over time.
2. Can moderate drinking still cause inflammation?
Yes. Even moderate alcohol use can temporarily increase inflammatory markers, especially in sensitive individuals. While effects may be short-lived, repeated exposure can lead to cumulative inflammation. Individual factors such as stress, diet, and sleep strongly influence how the body responds.
3. Does alcohol-related inflammation affect mental?
Alcohol-related inflammation can contribute to anxiety, low mood, irritability, and sleep disruption. Neuroinflammation interferes with stress-regulation systems in the brain. Over time, this can worsen emotional resilience and make it harder to manage daily stress without external support.
4. How long does inflammation last after drinking alcohol?
Short-term inflammation may last twenty-four to forty-eight hours after drinking. After prolonged or heavy use, inflammatory responses can persist much longer. Recovery timelines vary depending on status, drinking patterns, and whether supportive lifestyle or recovery changes are implemented.
5. Can stopping alcohol reduce inflammation?
Yes. Reducing or stopping alcohol allows inflammatory markers to decrease gradually. Many people notice improvements in energy, digestion, mood, and sleep within weeks. Long-term recovery further supports immune balance, especially when combined with stress reduction and consistent routines.
6. When should I seek help for alcohol-related inflammation?
Consider seeking help if inflammation-related symptoms persist, worsen, or interfere with daily life. Support is especially important if alcohol is used to cope with stress or emotional discomfort. Behavioral guidance can help address underlying patterns and promote whole-body recovery.